Last Updated on 27th September 2023
The phrase ‘dark web’ might bring up all sorts of connotations in your mind, none of which are probably good. For most people, the dark web is a place never ventured to or even given much thought. It’s the other side of the internet, the shadowy depths where criminals and people who are up to no good virtually reside.
Let’s take a look at the dark web, examine its uses, and discuss how you can protect the children in your care from its risks.

What is the Dark Web?
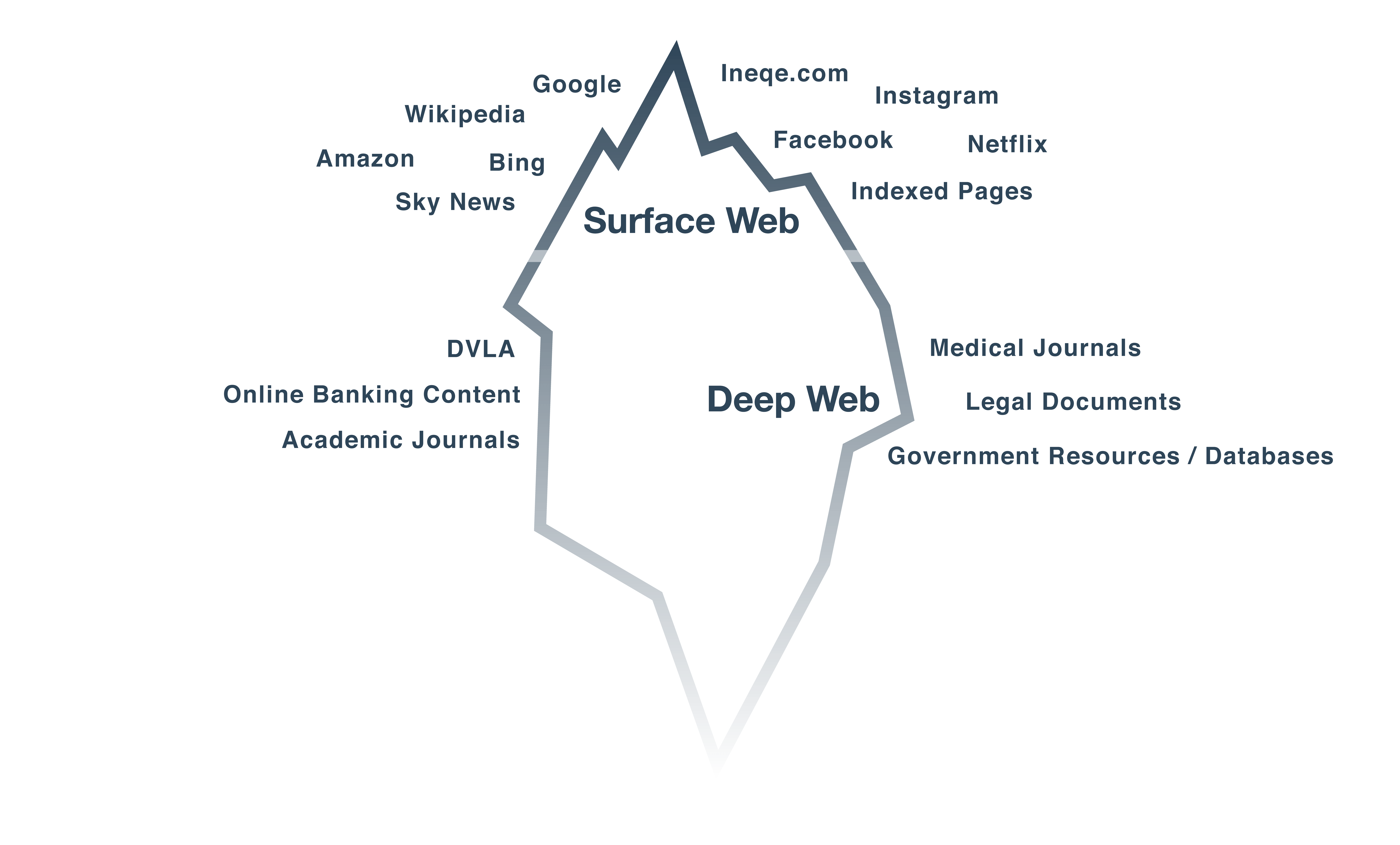
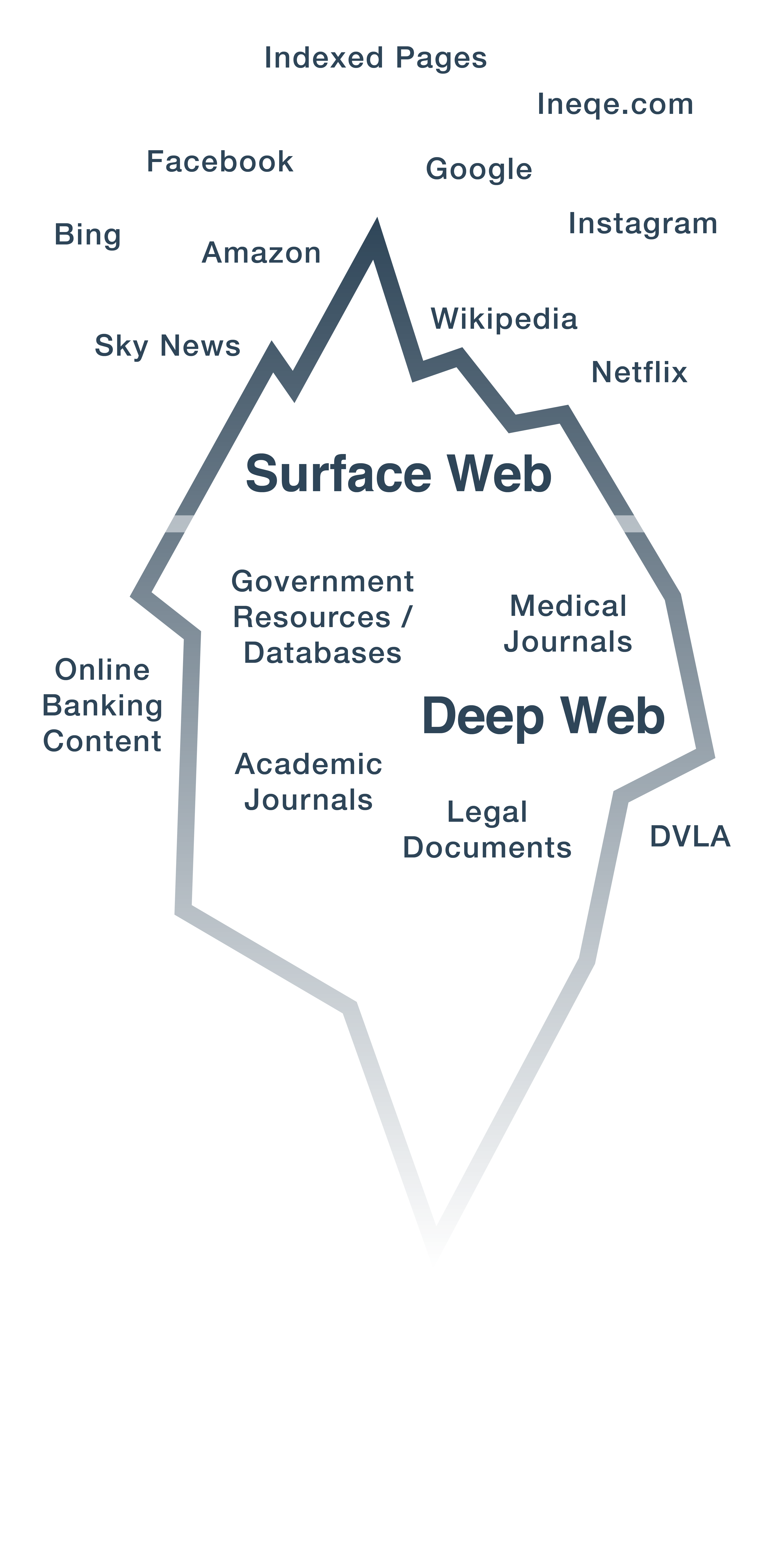
You may have heard the terms deep web and dark web used interchangeably. In fact, they are two different terms with separate meanings.
The deep web is any part of the internet that isn’t open and indexed. In other words, it’s websites or pages that won’t show up through internet searches because they aren’t designed to be public. It includes private information, like your email account and school web pages (usually referred to as ‘intranets’).
The dark web is the place where things are purposely hidden from view through encryption software, which can hide the identity and location of users. While it may seem like a big and unknowable place, the dark web only makes up a small part of the deep web.
Deep or Dark?

How is it accessed?
Tor Browser
What is it used for?
The dark web is used for many things, from trading illegal materials to confidential communication between news outlets and whistle-blowers. Young people can decide to access the dark web for various reasons, which include both legal and illegal motivations:

Should you be worried?
For many young people, the online world has become an important part of their every day. It’s a private place, with no parents there to watch what they do and say. This is especially true of the dark web. It’s a place a young person may (falsely) believe they can interact without obvious consequences, a space without family rules, without societal rules, and without government rules.
However, the dark web also requires a complex understanding of encryption, computers, and the internet. This means that if a young person does begin to use the dark web, they may not use it long term.
This is not a widespread issue. Some young people may hear about the dark web from videos with catchy titles like ’10 disturbing things hidden on the dark web’ or see it depicted in T.V. shows, like Netflix’s How to Sell Drugs Online (Fast), which may encourage curiosity.
If a young person decides to visit the dark web with relatively good intentions, there are still risks that can impact them including:
Join our Safeguarding Hub Newsletter Network
Members of our network receive weekly updates on the trends, risks and threats to children and young people online.